People working on this:
David Asner,
Bostjan Golob,
Brian Petersen,
Milind Purohit,
Alan Schwartz
For a complete list of references click
here
For world average values of measured observables (used below) click
here
Notation: the mass eigenstates are denoted
D 1 ≡ p|D0> +
q|D0> and
D 2 ≡ p|D0> −
q|D0>;
R D is the ratio of magnitudes of
D0
→ f and D0 → f amplitudes;
δ and δ2 are strong phase differences
between
D0
→ f and D0 → f amplitudes, and
φ is a weak phase difference.
The mixing parameters are defined as
x ≡ (m2 − m1)/Γ and
y ≡ (Γ2 − Γ1)/(2Γ), where
Γ = (Γ1 + Γ2)/2.
In the absence of CP violation, our convention is
x = (mCP+ − mCP−)/Γ,
y = (ΓCP+ − ΓCP−)/(2Γ), and
δ =
δ D0 → K−n(π)
−
δ D0
→ K−n(π) .
Allowing for CP violation, there are a total of 8 underlying parameters:
x, y, δ, δ 2 ,
R D, A D, |q/p|, and φ
From all experiments, there are currently 26 observables:
y CP ,
A Γ ,
x
K0S π+ π − ,
y
K0S π+ π − ,
|q/p|
K0S π+ π − ,
Arg(q/p) = φ
K0S π+ π −
(R M ) semileptonic ,
(x)
K+ π− π 0 ,
(y)
K+ π− π 0 ,
(R M )
K+ π− π
+ π − ,
(R M ) Ψ(3770) ,
(y) Ψ(3770) ,
(R D ) Ψ(3770) ,
(R D 1/2 cos δ) Ψ(3770) ,
(R D) BaBar ,
(A D) BaBar ,
(x'±, y'±) BaBar ,
(R D) Belle ,
(A D) Belle ,
(x'±, y'±) Belle ,
The relationships between these observables and the underlying
parameters are given below; the observables appear in
blue
(on the left sides of the equations), the underlying parameters in
magenta
(on the right sides), and intermediate variables in black.

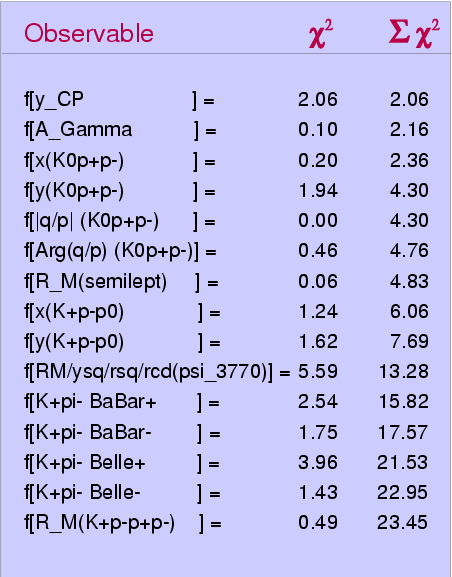
Observables used:
| Index | Observable | Value | Source | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | y CP | (1.132 ± 0.266)% | World average (COMBOS combination) of D0 → K+ K− / π+ π − results | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | A Γ | (0.123 ± 0.248)% | World average (COMBOS combination) of D0 → K+ K− / π+ π − results | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
No CPV:
World average (COMBOS combination)
of
D0 → K0 π+π −
results CPV-allowed: Belle D0 → K0 S π+ π − results; correlation coefficients:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | R M | (0.0173 ± 0.0387)% | World average (COMBOS combination) of D0 → K+l− ν results | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | R M | (0.019 ± 0.0161)% | BaBar K+ π − π + π − result | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 |
|
|
CLEOc Ψ(3770) results; correlation coefficients:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 |
|
|
BaBar
K+ π − results; correlation coefficients:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 |
|
| BaBar K+ π − results; correlation coefficients same as above. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 |
|
|
Belle
K+ π − results; correlation coefficients:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 |
|
| Belle K+ π − results; correlation coefficients same as above. |
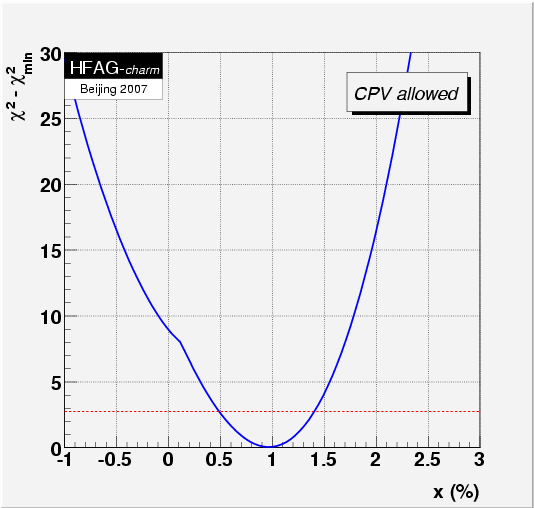
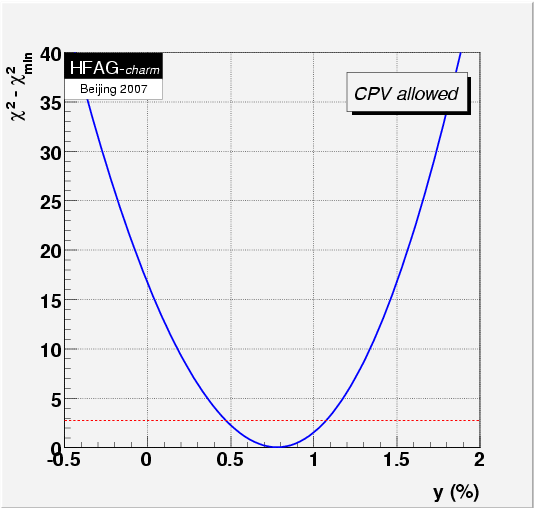
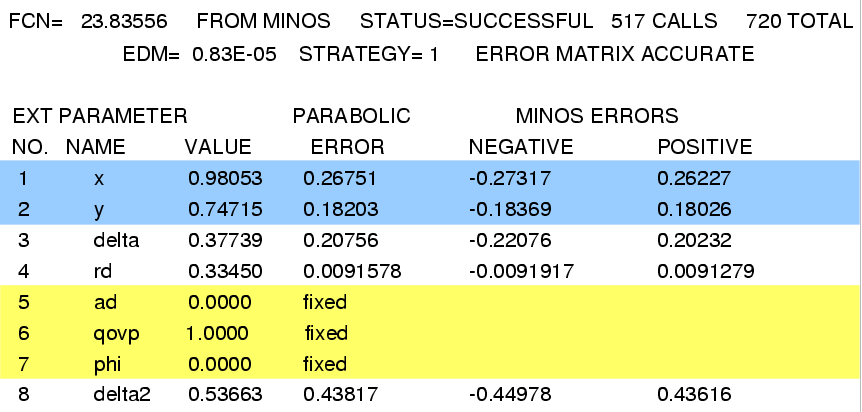
MINUIT fit results: note that x, y, R D, and A D are in percent; δ, δ2, and φ are in radians.
Fit #1, no CP violation (AD=0, |q/p|=1, φ=0, fixed):
Fit #2, no direct CP violation (AD=0, fixed):
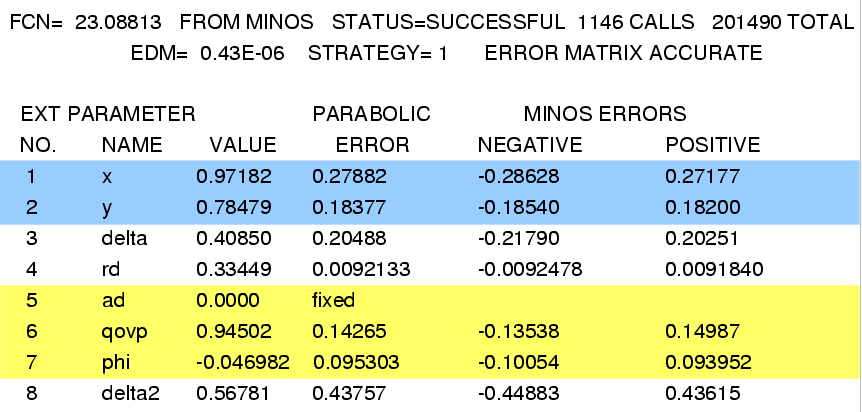
Fit #3, allowing direct CP violation (i.e., all parameters floated):
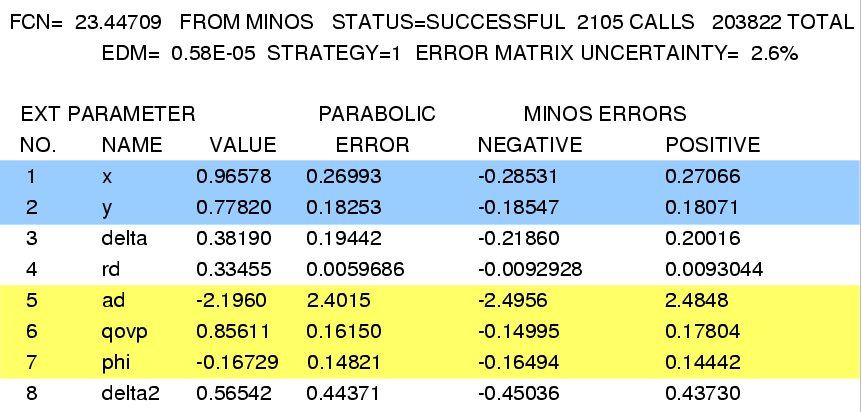
The final results allowing for CPV are:
x = (0.97 +0.27 −0.29 )%,
y = (0.78 +0.18 −0.19 )%,
δ = (0.38 +0.20 −0.22 ) radian,
δ2 = (0.57 +0.44 −0.45 ) radian,
R D = (0.335 ± 0.009)%,
A D = (−2.2 ± 2.5)%,
|q/p| = 0.86 +0.18 −0.15 ,
φ = (−0.17 +0.14 −0.16 ) radians.
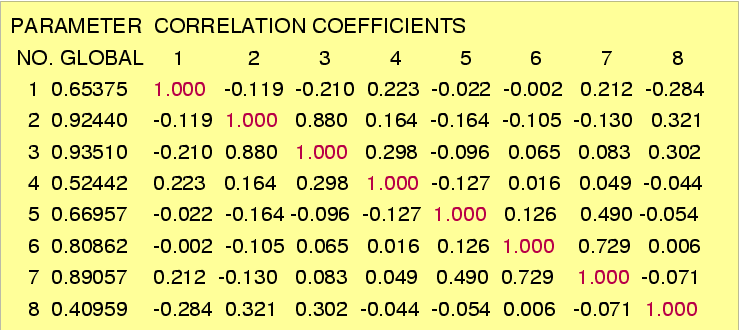
MIGRAD correlation coefficients:
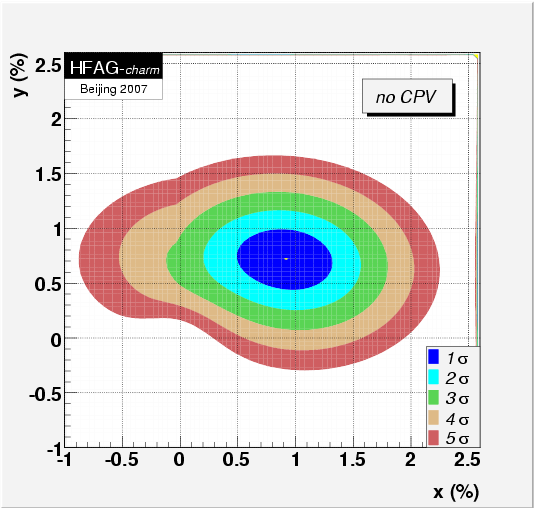
MNCONTOUR-like 2-d plots:
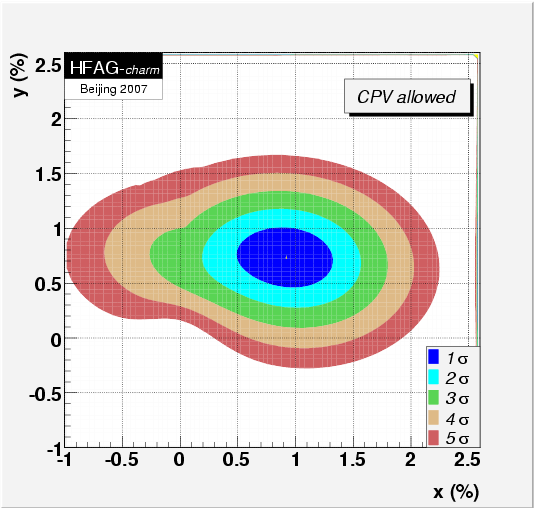
MNCONTOUR-like 1-d plots: red dashed horizontal line denotes Δχ 2 = 2.70, corresponding to 90% C.L. Cusp points result from multiple solutions.